Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows orthopedic surgeons to visualize, diagnose, and treat problems within a joint. It involves using a small, flexible instrument called an arthroscope, which contains a camera and a light source, to examine the inside of the joint without the need for large incisions.
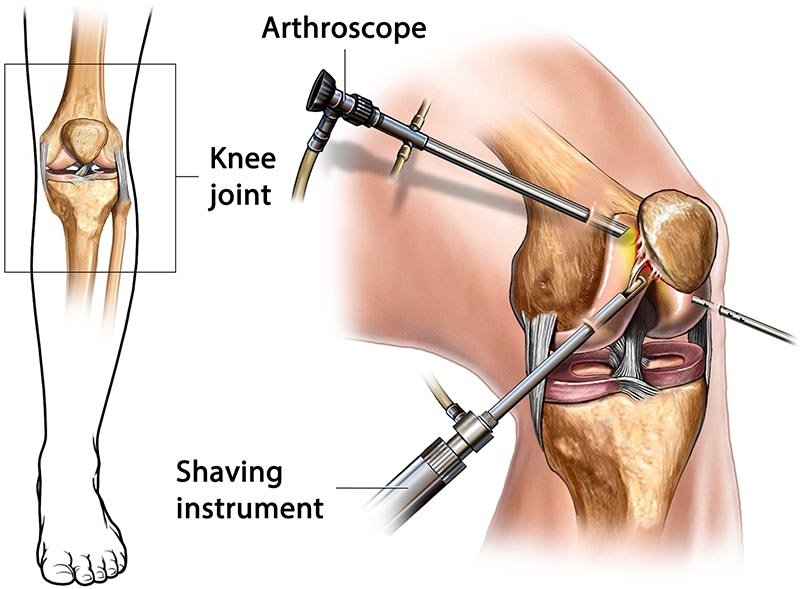
- Knee Arthroscopy: Knee arthroscopy is one of the most frequently performed types of arthroscopic procedures.
- Shoulder Arthroscopy: Shoulder arthroscopy is used to diagnose and treat various shoulder conditions, such as rotator cuff tears, labral tears, impingement syndrome, shoulder instability, and arthritis.
- Hip Arthroscopy: Hip arthroscopy is a specialized procedure that allows surgeons to access and treat hip joint problems.
- Ankle Arthroscopy: Ankle arthroscopy is utilized to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the ankle joint, including cartilage lesions, loose bodies, synovitis, and certain ligament injuries.
- Elbow Arthroscopy: Elbow arthroscopy is employed for diagnosing and treating various elbow joint disorders, including tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), loose bodies, and synovitis.
- Wrist Arthroscopy: Wrist arthroscopy is used to assess and treat conditions affecting the wrist joint, such as ligament injuries, triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears, and cartilage defects.
Symptoms
- Joint Pain: Persistent or recurrent pain in the joint, which may be caused by various conditions like cartilage injuries, ligament tears, or inflammation.
- Swelling: Swelling in or around the joint, can result from joint inflammation, damaged cartilage, or fluid accumulation.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty or reduced ability to move the joint through its full range of motion due to structural problems or injuries.
- Joint Instability: Feeling of the joint “giving way” or instability, which can be caused by ligament injuries or loose bodies within the joint.
- Locking or Catching Sensation: Sensation of the joint getting stuck or catching during movement, often associated with loose fragments or torn cartilage.
- Clicking or Popping Sounds: Audible noises during joint movement, which can occur due to cartilage abnormalities or other mechanical issues.
- Recurrent Joint Effusions: Repeated fluid build-up in the joint, often seen in conditions like synovitis or meniscal tears.
- Diagnostic Confirmation: Arthroscopy is also used for diagnostic purposes when the cause of joint symptoms is unclear or not adequately assessed through non-invasive imaging techniques like X-rays or MRI.
Treatment
- Meniscus Tears: In the knee, arthroscopy can be used to repair or remove damaged meniscus (cartilage) that cushions the joint.
- Ligament Tears: Arthroscopic surgery can repair or reconstruct torn ligaments, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or the rotator cuff in the shoulder.
- Cartilage Damage: Arthroscopy allows the surgeon to trim, repair, or regenerate damaged cartilage in various joints.
- Joint Debridement: Arthroscopic debridement involves removing loose or damaged tissue from the joint, which can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Synovectomy: This procedure involves removing inflamed or abnormal synovium (joint lining) seen in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Removal of Loose Bodies: Arthroscopy can be used to remove loose bone fragments or cartilage that may be causing pain and limited joint movement.
- Impingement Syndrome: In the shoulder, arthroscopy can address impingement caused by the compression of tendons and muscles.
Benefits
- Minimally Invasive: Arthroscopic surgery requires only small incisions, resulting in less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: The arthroscope provides the surgeon with a clear view of the joint’s internal structures, allowing for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
- Reduced Pain: Patients typically experience less post-operative pain compared to open surgeries, which may lead to a quicker return to normal activities.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Due to the minimally invasive nature of arthroscopy, most patients can resume their normal activities and physical therapy sooner than with open surgery.
- Outpatient Procedure: Many arthroscopic surgeries are performed on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can return home on the same day of the procedure.
Precautions
- Avoid Driving: Avoid driving until you have approval from your surgeon, as the effects of anesthesia and pain medications can impair your reflexes.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Alcohol and smoking can interfere with the healing process. It’s best to avoid them during the recovery period.
