Shoulder Surgery
Shoulder surgery is a medical procedure performed to address various shoulder joint problems, including injuries, degenerative conditions, and chronic shoulder pain. There are several types of shoulder surgeries, each tailored to specific conditions and individual patient needs. Below are some common types of shoulder surgeries and essential information about each:
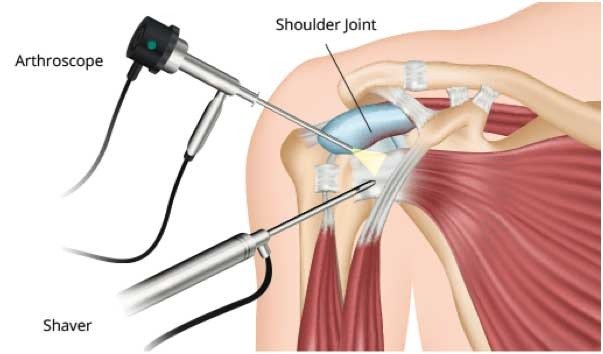
Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery: Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves using a tiny camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments inserted through small incisions in the shoulder. Arthroscopic shoulder surgery is used to diagnose and treat various shoulder issues, such as rotator cuff tears, labral tears, impingement, and shoulder instability. This type of surgery typically results in smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Symptoms
- Pain: Pain is a typical symptom after shoulder surgery. The intensity and duration of pain can vary based on the type of surgery and the individual’s pain tolerance. Pain is usually managed with prescribed pain medications and gradually subsides as the healing process progresses.
- Swelling: Swelling around the surgical site is common after shoulder surgery. Elevating the arm and using ice packs can help reduce swelling during the initial recovery phase.
- Stiffness: Patients may experience stiffness in the shoulder joint and surrounding muscles after surgery. Physical therapy and prescribed exercises are essential to improve range of motion and reduce stiffness.
- Bruising: Bruising around the surgical area may occur, especially if the surgery involved cutting through the skin and tissues. The bruising generally resolves on its own over time.
- Weakness: The operated shoulder may feel weak or unstable initially. Physical therapy will focus on strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint to restore stability and function.
Treatment
Arthroscopic Surgery: Arthroscopic shoulder surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the use of a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments to diagnose and treat various shoulder conditions. It is commonly used for procedures such as rotator cuff repair, labrum repair, and removal of bone spurs or loose cartilage.
Rotator Cuff Repair: This surgical procedure is performed to repair a torn rotator cuff tendon in the shoulder. The surgeon may reattach the torn tendon to the bone using sutures or anchors.
Labrum Repair: A labrum tear in the shoulder, commonly known as a SLAP tear, can be repaired through arthroscopic surgery. The surgeon reattaches the torn labrum to its original position on the glenoid (socket) of the shoulder joint.
Shoulder Stabilization: In cases of shoulder instability or recurrent dislocations, shoulder stabilization surgery is performed. This procedure tightens and repairs the damaged ligaments and tendons to prevent dislocations.
Total Shoulder Replacement: Total shoulder replacement (arthroplasty) is performed to replace the damaged or arthritic shoulder joint with a prosthetic joint. The procedure involves replacing the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) and the glenoid (socket) with artificial components.
Precautions
Avoid Sudden Movements: During the early recovery period, avoid sudden movements or heavy lifting with the affected arm to prevent stress on the surgical site.
Physical Therapy: Engage in physical therapy sessions as prescribed by your healthcare team. Physical therapy helps improve shoulder strength, range of motion, and overall function during the recovery process.
Pain Management: Take prescribed pain medications as directed to manage post-operative pain. It’s essential to stay ahead of the pain to facilitate your participation in physical therapy and daily activities.
Gentle Exercises: Perform the recommended gentle exercises and stretches provided by your physical therapist to prevent shoulder stiffness and improve mobility.
